What does E7015 stand for?
E7015 is a very important low-hydrogen sodium electrode, widely used in welding, especially in applications requiring high weld quality.What does E7015 stand for?
1. Model Explanation: What does E7015 stand for?
“E7015” is a model designation used in both the American Standard (AWS A5.1) and the Chinese National Standard (GB/T 5117). Let’s break it down:
▶E: Indicates an arc welding electrode.
▶70: Indicates a minimum tensile strength of the deposited metal of 70 ksi (kilopounds per square inch). Converted to metric units, this translates to approximately 490 MPa. This means welds made with this electrode are extremely strong.
▶1: Indicates it is suitable for all-position welding, including flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead welding.
▶15: Indicates the electrode’s coating type and welding current.
▶Important Note: In the Chinese standard (GB/T 5117), E7015 corresponds to J507. In actual production and distribution, the name J507 is more commonly used.
2. Core Characteristics
① Low Hydrogen Type: This is the core characteristic of E7015. The coating composition strictly controls the moisture and hydrogen content, significantly reducing the risk of hydrogen-induced cracking (cold cracking) in the weld. This is crucial for welding high-strength steel, thick plates, or structures with high restraints.
② DC Reverse Connection (DC+): E7015 electrodes must be used with a DC power source, with the electrode connected to the positive terminal (DC+ or DCEP). This connection provides a more stable arc and deeper penetration. It cannot be used with alternating current (AC).
③ Excellent Mechanical Properties: The weld metal exhibits high strength, good ductility, and toughness.
④ Operability: The arc blow force is strong, resulting in deep penetration, but spatter is relatively small, and slag removability is excellent. Operability is excellent when welding in a vertical position.
3. Main Applications
▶Structures requiring high crack resistance: Such as ships, bridges, high-pressure vessels, and pipelines.
▶ Thick plate structures: Because thick plates are subject to high restraint stress during welding, cold cracks are more likely to occur.
▶ Structures operating in low-temperature environments: Welds must possess good impact toughness.
▶ Components requiring post-weld heat treatment: Such as stress relief annealing.
4. Usage Precautions (Very Important!)
Because these are low-hydrogen electrodes, their use and storage require stricter care than those of conventional acidic or calcium-titanium electrodes.
① Baking:
▶ New electrodes must be baked before use to remove moisture from the coating. Baking temperatures are typically between 300°C and 350°C for 1-2 hours.
▶ Opened or damp electrodes must also be rebaked.
② Insulation:
▶ After baking, electrodes should be immediately placed in an insulated container (electrode heat preservation barrel) maintained at 100°C to 150°C and removed from the container as needed.
▶ Welding rods removed from the heat preservation tube and exposed to the atmosphere for more than 4 hours generally require rebaking. Do not use damp welding rods.
③ Welding Procedure:
▶ Use short arc welding to better protect the weld pool and prevent air intrusion.
▶ Be sure to clean the grooves from oil, rust, and moisture, as these can also be sources of hydrogen.
5. Comparison with Other Common Welding Rods
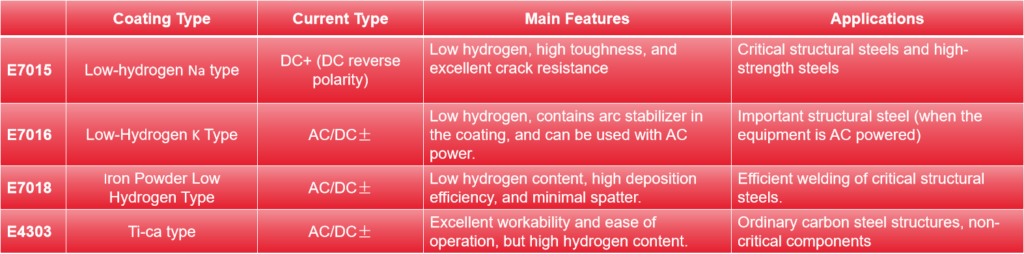
Summary
E7015 is a high-performance, low-hydrogen basic electrode known for its excellent crack resistance and superior weld mechanical properties. It is primarily used for welding carbon steel and low-alloy steel structures requiring extremely high quality. The key to its successful use lies in strict pre-welding drying and heat preservation measures, as well as the requirement for DC reverse power supply. If you are welding load-bearing structures, pressure vessels, or equipment working in harsh environments, E7015 is usually one of the preferred electrodes.


