
Carbon steel submerged arc welding wire
Carbon steel submerged arc welding wire is the filler metal used in submerged arc welding (SAW) processes for welding carbon steel. A key characteristic is that it must be used in conjunction with flux, which plays crucial roles in protection, purification, and alloying during the welding process.Carbon steel submerged arc welding wire
一. Classification and Types of Submerged Arc Welding Wires
The AWS standard classifies carbon steel SAW wires and fluxes as a whole system. Wire types typically begin with “F,” followed by a series of numbers and letters indicating the mechanical properties of the deposited metal formed when combined with a specific flux.
Example of wire type: F7A2-EM12K
● F: Indicates the wire type.
● 7: Indicates a minimum tensile strength of 70 ksi (approximately 482 MPa) in the deposited metal.
● A: Indicates the as-welded heat treatment condition.
● 2: Indicates the Charpy V-notch impact energy requirement at a specific temperature (typically 0°F or -20°C).
● EM12K: This is a unique designation for the wire itself. Common carbon steel submerged arc welding wire designations (e.g., EM12K, EL8, EH14):
These designations describe the chemical composition of the welding wire.
● “E” represents the electrode (welding wire).
● “L” represents low carbon.
● “M” represents medium manganese.
● “H” represents high manganese.
● “K” indicates the addition of potassium silicate, etc., to improve welding processability.
Common Combinations:
❶ EM12K / EL8 + AKJ431: This is one of the most classic and commonly used combinations. EM12K (medium manganese) welding wire combined with AKJ431 (high silicon, high fluorine) flux provides good welding processability and aesthetically pleasing weld formation, suitable for welding various low-carbon steel structures.
❷ EH14 + AKJ101: EH14 (high manganese) welding wire paired with sintered flux AKJ101 achieves higher weld metal toughness and better mechanical properties, commonly used in important steel structures such as pressure vessels, bridges, and ships.
二. Carbon steel submerged arc welding wire:Matching Principles of Welding Wire and Flux
This is the core of submerged arc welding technology. Different matches will produce completely different weld properties.
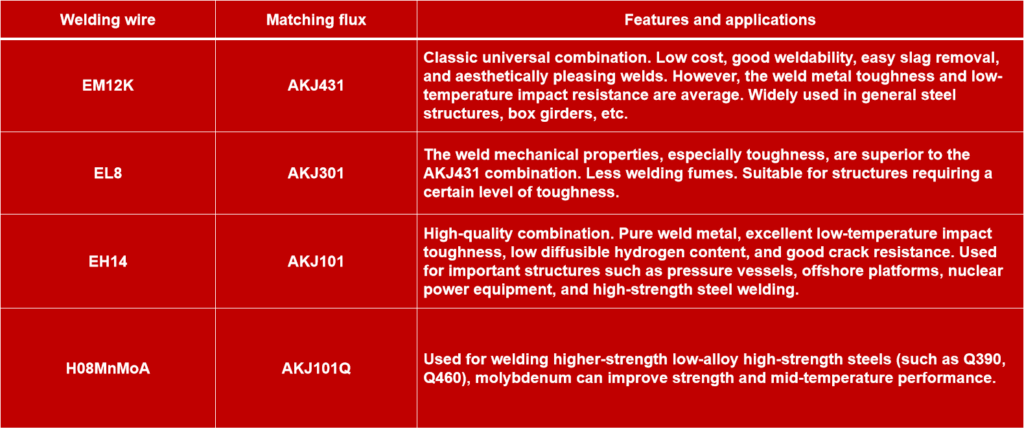
Selection Points:
❶ Based on base metal strength and requirements: The strength of the matched deposited metal should be equal to or slightly higher than that of the base metal.
❷ Based on toughness requirements: For important structures and equipment operating in low-temperature environments, alkaline fluxes (such as AKJ101) must be selected.
❸ Based on efficiency requirements: Iron powder type fluxes or welding wires can greatly improve deposition efficiency.
三. Common Specifications and Packaging of Submerged Arc Welding Wire
❶ Diameter: Common diameters include 2.0mm, 2.5mm, 3.0mm, 4.0mm, 5.0mm, and 6.0mm. Diameter selection depends on welding current and plate thickness.
❷ Packaging: Usually in spool form (welding wire spool), weighing 25kg, 50kg, etc., directly mounted on the submerged arc welding machine.
四. Carbon steel submerged arc welding wire:Application Areas
Carbon steel submerged arc welding is widely used due to its high efficiency and high quality in:
❶ Heavy steel structures: Building steel structures, bridges, iron towers.
❷ Pressure vessels: Boilers, storage tanks, chemical containers.
❸ Shipbuilding: Hull assembly.
❹ Pipelines: Double-wire or multi-wire welding of large-diameter long-distance pipelines.
❺ Construction machinery: Crane booms, excavator frames, etc.
五. Precautions for Use
❶ Storage of Welding Wire and Flux: They must be kept dry, especially the flux. Moisture in the flux can cause porosity and hydrogen-induced cracking in the weld. Sintered flux (such as AKJ101) typically needs to be dried at 250-350°C for 1-2 hours before use.
❷ Pre-welding Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the bevel and both sides to remove oil, rust, moisture, and other contaminants.
❸ Welding Parameters: Parameters such as current, voltage, and welding speed have a significant impact on weld formation and performance and must be determined according to the process qualification.
❹ Flux Layer Thickness: Too thin a layer may not provide complete protection, while too thick a layer may hinder gas escape and cause surface indentations.
六. Summary
Choosing carbon steel submerged arc welding wire is not an isolated act, but a process of selecting a “welding wire-flux system.”
❶ For ordinary steel structures, EM12K/AKJ431 or EL8/AKJ301 are economical and practical choices.
❷ For critical structures requiring high toughness and low crack risk, a combination of EH4/AKJ101 or equivalent AWS-level weld materials is a more reliable choice.
In actual production, welding materials should be selected strictly in accordance with product technical requirements and the qualified Welding Procedure Specification (WPS).

