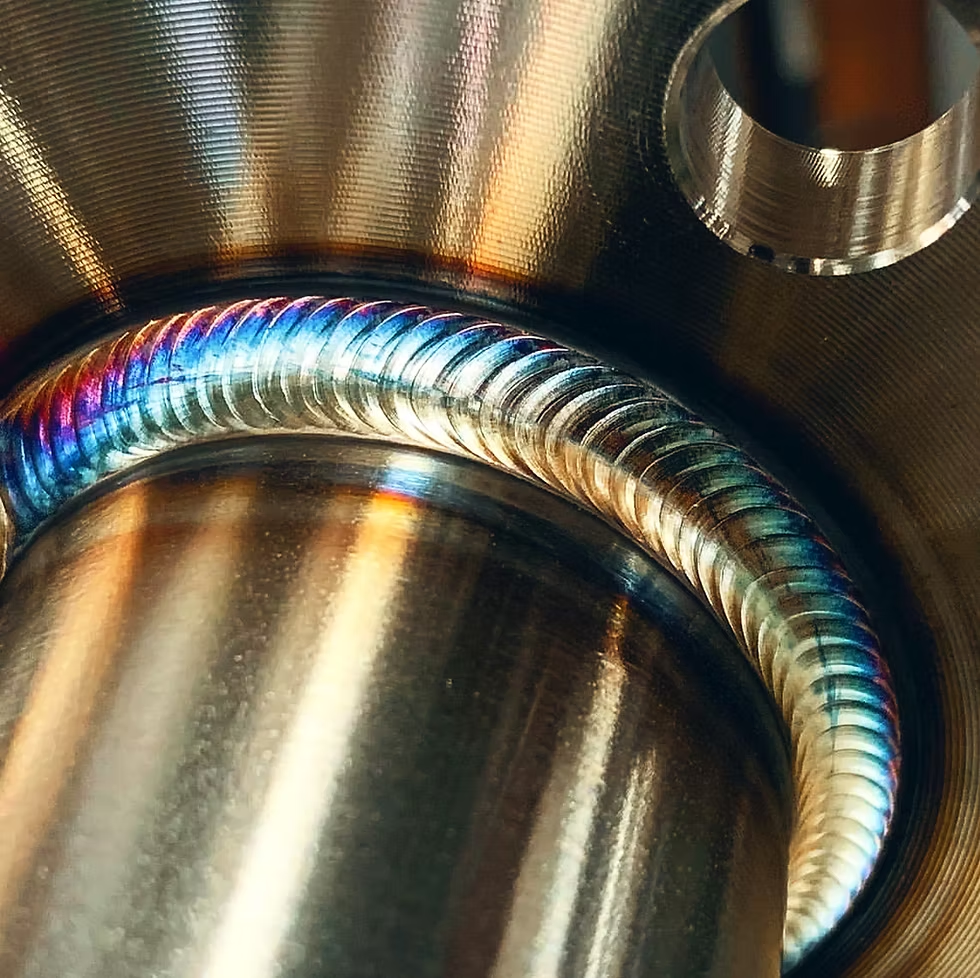
Learn about ER2594
ER2594 is the only correct choice for welding super duplex stainless steel.learn about ER2594
●ER: Like ER2209, this prefix is used in the US AWS A5.9/A5.4 standard to designate wire or filler rod for TIG/MIG welding.
●2594: The number represents its key alloying elements. 25 represents approximately 25% chromium (Cr), while 94 represents the combination of approximately 9.5% nickel (Ni) and 4% molybdenum (Mo). More importantly, it contains very high levels of nitrogen (N) (typically > 0.25%).
Simply put, ER2594 is a highly alloyed filler metal specifically designed for welding 25Cr series super-duplex stainless steels. Its chemical composition is optimized to ensure weld properties that match those of the base metal.
Click the link for ER2594 product information
learn about ER2594 :https://www.akweld.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/ER2594.pdf
一.Core Characteristics and Design Objectives:
Superduplex steels (such as S32750) contain higher levels of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen than standard duplex steels (such as S32205), resulting in higher strength and superior corrosion resistance (particularly pitting and crevice corrosion). ER2594 welding wire is designed to match and maintain this high performance.
1. “Superalloyed” Design: The chemical composition of ER2594 (particularly Ni, Mo, and N) is generally richer than that of the superduplex steel base material (such as S32750) it is welded to.
① Compensating for burnout: The high temperature of the welding arc can cause elements such as nitrogen (N) to burnout.
② Promoting Austenitization: Superduplex steels have a high chromium equivalent and a strong tendency to ferritize. Higher nickel and nitrogen contents are powerful austenite-forming elements, effectively promoting the precipitation of austenite (γ) from the ferrite (α) matrix during cooling, thereby offsetting the effects of rapid cooling and achieving a balanced phase ratio.
③ Guaranteed corrosion resistance: Ensure the weld metal’s PRE value (pitting resistance equivalent) is equal to or slightly higher than that of the base material to prevent the weld from becoming a weak link in corrosion.
2. Extremely high mechanical and corrosion properties: When properly welded, ER2594 weld metal can achieve:
① Very high strength: Room temperature tensile strength typically reaches ≥800 MPa.
② Excellent toughness.
③ Outstanding corrosion resistance: Exceptionally high resistance to chloride pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking.
二. Main Applications (What Materials Are Welded?):
Learn about ER2594 is specifically designed for welding 25% Cr super-duplex stainless steel. The most typical grades are:



Important Notes:
① Never use ER2209 welding wire to weld super-duplex steel. The insufficient alloy content of ER2209 can lead to an imbalanced weld metal phase balance (excessive ferrite), insufficient strength, and, in particular, a severe decrease in corrosion resistance, effectively weakening the entire structure.
② Conversely, ER2594 is generally not recommended for welding standard duplex steels (such as 2205) unless exceptional strength is required, and cost and the significant difference in weld chemistry from the base material are considered.
三. Other Compatible Welding Materials:
Similar to ER2209, the same chemical composition is also found in other welding materials:




四. Key Process Points for Welding with ER2594 (More Stringent Than ER2209!):
The process window for welding super-duplex steel is narrower, and the control requirements are more stringent.
1. Shielding Gas:
① High-purity argon (Ar ≥ 99.995%) must be used.
② Root back protection: Critical! A mixture of Ar and nitrogen (N₂) must be used, with a recommended ratio of Ar + 2-5% N₂. Nitrogen addition is crucial to compensate for nitrogen loss in the root weld of super duplex steel and ensure austenitization.
2. Heat input control: This requires more precise control. The range is typically between 0.5-1.5 kJ/mm. The recommended parameters provided by the welding material manufacturer must be strictly adhered to.
3. Interpass temperature control: This is the most critical factor and requires extremely strict requirements! It must be strictly controlled below 80°C-100°C (the specific limit should be referenced in the WPS, but it is generally lower than the 100°C for standard duplex steel). A temperature gauge must be used to measure each pass to ensure adequate cooling.
4. Preheating and postheating: Preheating is strictly prohibited. Any form of post-weld heat treatment is also strictly prohibited within the temperature range sensitive to σ phase precipitation (approximately 600-1000°C).
5. Cleanliness: There is zero tolerance for contaminants such as oil, grease, moisture, and paint. Any contamination will degrade weld performance.
五. Post-weld Inspection:
Super-duplex steel welds require even more stringent inspection requirements:
① Non-destructive Testing (NDT): 100% RT or UT.
② Metallographic Examination: Mandatory. Must check:

③ Mechanical Testing: Tensile, bend, and low-temperature impact testing (typically requiring -46°C Charpy V impact).
④ Corrosion Testing: Pitting corrosion resistance testing (ASTM G48 Method A) is typically required to verify that the weld meets corrosion resistance standards.
Summary Comparison: ER2594 vs. ER2209
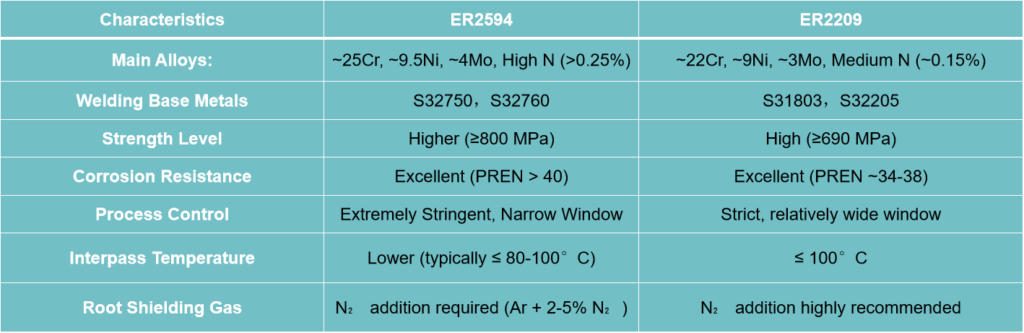
Conclusion:
ER2594 is the only correct choice for welding super duplex stainless steel. Its use requires a higher level of welding technology and more stringent quality control. Any deviation from the process parameters could result in seriously unacceptable weld performance. A comprehensive welding procedure qualification (WPS/PQR) must be conducted before actual use, and the weld must be operated under the strict supervision of an experienced welder.


