
Which Welding Materials Are Used in Oil and Gas Pipelines?
“In the oil and gas industry, a single weld can mean the difference between safe, reliable operations and costly failures—choosing the right materials is not optional, it’s mission-critical.” Welding Materials in Oil and Gas Pipelines
1. Welding Materials in Oil and Gas Pipelines:Introduction: Why Welding Materials Matter in Pipelines
Oil and gas pipelines operate under extreme conditions—high pressures, fluctuating temperatures, corrosive environments, and sometimes remote locations. Selecting the proper welding materials ensures:
Structural integrity
Leak prevention
Corrosion resistance
Compliance with international codes and standards
A wrong choice could compromise pipeline safety and lead to catastrophic consequences.
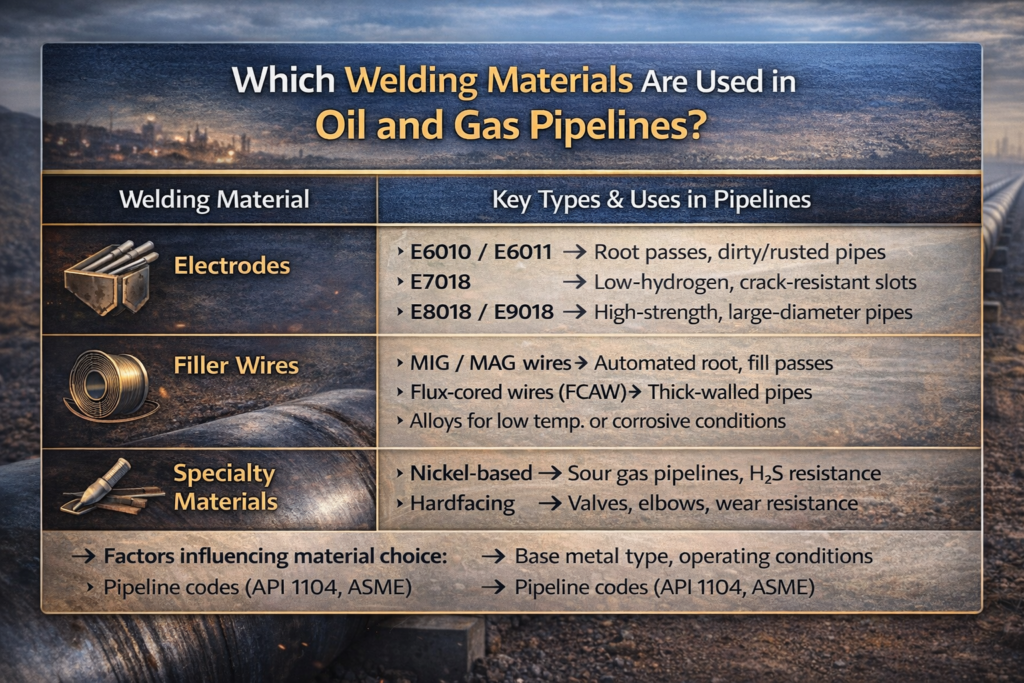
2. Welding Materials in Oil and Gas Pipelines:Common Welding Materials for Pipelines
a) Electrodes
E6010 / E6011: Deep penetration for root passes, ideal for dirty or rusted pipes
E7018: Low-hydrogen electrode for high-strength, crack-resistant welds
E8018 / E9018: Special high-strength applications, especially for large-diameter pipelines
b) Filler Wires
MIG / MAG wires: Often used in automated pipeline welding
Flux-cored wires (FCAW): High deposition rates, suitable for thick pipes
Alloy-specific wires for low-temperature or high-corrosion pipelines
c) Specialty Materials
Nickel-based electrodes: For corrosion-resistant pipelines transporting sour gas (H₂S)
Hardfacing rods: Applied on valves or elbows to resist erosion and wear
3. Welding Materials in Oil and Gas Pipelines:Factors Influencing Material Selection
Base Metal Type – Carbon steel, stainless steel, or nickel alloys
Operating Conditions – Pressure, temperature, and corrosive environments
Pipeline Codes & Standards – ASME, API 1104, ISO 3183
Welding Position & Accessibility – Field welds vs. shop fabrication
Cost and Availability – Balancing performance and supply chain reliability
4. Welding Materials in Oil and Gas Pipelines:Best Practices for Pipeline Welding
Maintain low-hydrogen conditions to prevent cracking
Preheat and post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) as required
Conduct non-destructive testing (NDT) on critical joints
Keep electrodes and wires dry with proper storage
5. Conclusion: Welding Materials Are Pipeline Lifelines
Choosing the right welding materials is not just a technical detail—it’s the backbone of pipeline safety, efficiency, and longevity. Oil and gas companies, EPC contractors, and welding service providers must invest in quality, traceability, and expertise to avoid costly failures.

